Water treatment
Water treatment refers to the process of improving the quality of water to make it suitable for a specific purpose, such as drinking, industrial processes, agriculture, or recreational activities. The goal of water treatment is to remove contaminants, such as harmful bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and suspended solids, to ensure the water is safe and clean for its intended use. This process is vital not only for protecting human health but also for supporting agricultural productivity, maintaining ecosystem balance, and providing safe water for industrial applications.
Green Genesis Engineering Ltd. is a specialized engineering company offering tailored water and wastewater solutions across various industries and domestic applications.
Since 2007, we have been at the forefront of delivering innovative and sustainable solutions for diverse water treatment applications, wastewater reuse, and membrane separation processes. Our extensive range of advanced technologies, combined with deep expertise across all water-related sectors, ensures that we provide cost-effective solutions that meet and exceed your water quality requirements.
This version emphasizes the company’s specialization, experience, and commitment to innovation and sustainability. It also highlights the range and depth of expertise offered.
Types of Water treatment
1. Drinking Water treatment:
Drinking water treatment is the process of purifying water to make it safe for human consumption, eliminating any short-term or long-term risks of adverse health effects. The treatment typically involves multiple stages to remove contaminants such as bacteria, algae, viruses, fungi, and minerals like iron and manganese. Drinking water treatment aims to ensure that the water meets safety standards and is free from harmful substances, making it safe for daily consumption.
2. Industrial Water Treatment:
Industrial water treatment refers to the processes used to optimize water-based industrial operations, such as heating, cooling, washing and processing, cleaning, in order to reduce operating costs and mitigate risks. This treatment prevents water from causing damage to equipment, such as scaling and corrosion in steam boilers and cooling towers, which can lead to increased fuel consumption and the proliferation of harmful bacteria. Additionally, industrial water treatment ensures the quality of water in direct contact with manufactured products, preventing defects in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, beverages, and pharmaceuticals.
3. Waste Water Treatment
Wastewater treatment is the process of removing and eliminating contaminants from wastewater, converting it into an effluent that can be safely returned to the water cycle or reused. This process occurs in a wastewater treatment plant, which is designed to treat various types of wastewaters, including domestic (or municipal) wastewater, industrial wastewater, agricultural wastewater, and leachate.
Benefits of Water treatment
Water treatment plants are critical infrastructure for providing safe drinking water and treating wastewater to protect the environment. Water treatment plants are crucial for public health & environmental protection for several reasons:
- Removal of Contaminants: They eliminate harmful contaminants from water, including pathogens (bacteria, viruses, and parasites), chemicals (pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial pollutants), and physical impurities (sediments and debris).
- Prevention of Waterborne Diseases: By removing pathogens, water treatment plants help prevent diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid fever, which can spread through contaminated water.
- Provision of Safe Drinking Water: They ensure that the water supplied to the public meets safety standards and is free from harmful levels of contaminants, making it safe for consumption.
- Improvement of Water Quality: Treatment processes enhance the taste, odor, and appearance of water, making it more palatable and acceptable for everyday use.
- Support for Public Hygiene and Sanitation: Access to clean water is essential for maintaining hygiene and sanitation practices, such as handwashing, bathing, and food preparation, which are critical for preventing the spread of infectious diseases.
- Environmental Protection: Environmental protection is crucial for sustaining ecosystems, human health, and the overall quality of life on Earth. One of the key aspects of environmental protection is water treatment, which plays a significant role in preserving water resources and ensuring clean water availability for various uses.
Process of Water Treatment
The process typically involves several stages, each targeting different types of impurities. Common steps include:
Coagulation and Flocculation:
Coagulation and flocculation are essential processes used in water and wastewater treatment to remove suspended solids, organic matter, and other contaminants, making the water clearer and safer for consumption or discharge.
The most common coagulants are aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride (PAC). These chemicals are positively charged and neutralize the negative charges on suspended particles.
Flocculants: Sometimes, additional chemicals called flocculants (polymers) are added to enhance the aggregation of particles. These can be either cationic, anionic, or non-ionic polymers, depending on the nature of the suspended particles.
After coagulation and flocculation, the water is often allowed to sit in a sedimentation basin where the large flocs can settle out of the water by gravity. The settled particles form a sludge layer at the bottom, which can then be removed
Sedimentation:
Sedimentation is a key water treatment process that involves the separation of suspended particles from a fluid using gravity settling. In this process, the water velocity is reduced, allowing particles to remain stable under quiescent conditions. As a result, the particles gradually settle out of the suspension due to gravitational force, leading to the removal of suspended solids trapped in the floc.
Filtration:
Filtration is a critical technique in water treatment, aimed at removing pollutants and contaminants based on their particle size. By efficiently eliminating these impurities, filtration not only enhances water quality but also enables the treated water to be reused for various purposes, including industrial processes, irrigation, and even potable water supplies. The effectiveness of the filtration process largely depends on the type and nature of the contaminants present in the wastewater, which determines the selection of the appropriate filtration method.
There are two primary forms of water filtration: particle filtration and membrane filtration.
Particle Filtration:
This method involves the removal of suspended solids and larger particulate matter from the water. It typically employs media filters, such as sand, gravel, or activated carbon, which trap particles as water passes through. Particle filtration is often used as a preliminary step in wastewater treatment to reduce the load of contaminants before more advanced filtration or purification processes.
Membrane Filtration:
This advanced filtration technique uses semi-permeable membranes to separate contaminants at a molecular level. Depending on the pore size of the membrane, various types of pollutants, including bacteria, viruses, and dissolved salts, can be effectively removed. Membrane filtration is highly effective for producing high-quality water, making it suitable for applications where stringent water purity standards are required.
Disinfection:
Disinfection is a crucial step in the treatment of water and wastewater, designed to eliminate or deactivate harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, that can cause waterborne diseases. The process ensures that water is safe for human consumption or can be safely discharged into the environment. Here’s a breakdown of the main methods and considerations in disinfection for water and wastewater treatment:
Chlorination: Chlorine is added to water in various forms, such as chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, or calcium hypochlorite.
Ozonation: Ozone gas (O₃) is generated on-site and injected into the water, where it reacts with organic and inorganic materials.
Ultraviolet (UV) Irradiation: Water passes through a UV light chamber where microorganisms are inactivated by UV radiation.
Ion Exchange:
Ion exchange is a widely used process in water treatment, particularly for softening and demineralizing water. The process relies on resins, which are insoluble substances capable of exchanging specific ions in the water with ions from the resin. This exchange occurs without altering the resin’s overall structure, making the process both efficient and reversible.
Ion exchange is a versatile and effective method for treating water, particularly in applications requiring the removal of specific ions to prevent scaling, corrosion, or to achieve high-purity water. The reversibility and reusability of the resin make it a sustainable option for long-term water treatment needs.
Ion Exchange Resins:
Cation Exchange Resins: These resins have negatively charged functional groups and exchange cations (positively charged ions) in the water, such as calcium (Ca²⁺), magnesium (Mg²⁺), and iron (Fe²⁺), with hydrogen (H⁺) or sodium (Na⁺) ions from the resin.
Anion Exchange Resins: These resins have positively charged functional groups and exchange anions (negatively charged ions) like chloride (Cl⁻), sulfate (SO₄²⁻), and nitrate (NO₃⁻) with hydroxide (OH⁻) ions from the resin.
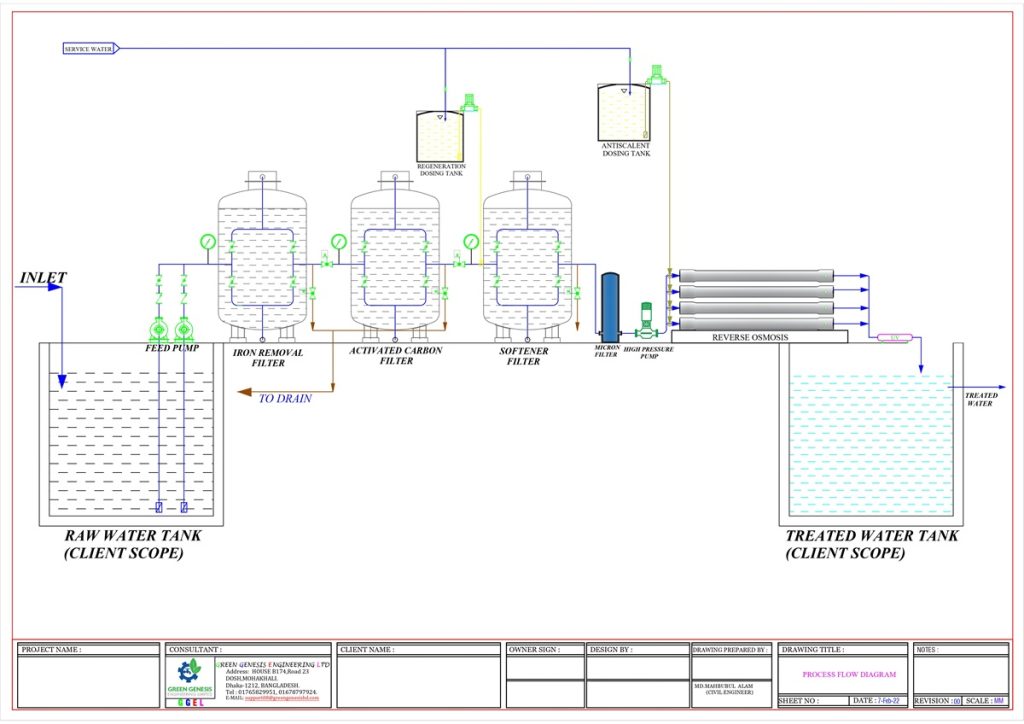
Reverse Osmosis (RO):
Reverse osmosis (RO) stands as an indispensable water purification technique, utilizing a semi-permeable membrane to eliminate dissolved minerals, organic and inorganic compounds, heavy metals, as well as microbial contaminants such as bacteria and viruses. Widely employed in industrial processes and potable water production, RO functions by exerting reverse osmotic pressure on water, compelling it through the membrane, thereby capturing impurities while allowing clean water passage. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure counteracts the natural osmotic pressure, driving water from areas of high contaminant concentration to regions of low concentration, effectively reversing the natural flow. However, before reaching the clean water side, it must pass through a specialized filter, where contaminants are captured, permitting only purified water to proceed. This meticulous process ensures the production of exceptionally clean drinking water, meeting the desired standards of purity. This method finds extensive use in households and industries for generating safe, drinkable water.
RO is most commonly known for its use in drinking water purification from seawater, removing the salt and other effluent materials from the water molecules.
Desalination:
Desalination is the process of removing salts and other impurities from seawater or brackish water to produce fresh water suitable for human consumption, agriculture, and industrial use. This process is critical in regions where freshwater resources are scarce or contaminated, providing an alternative source of clean water. Desalination plays a vital role in addressing global water challenges, particularly water-stressed regions, but it requires careful consideration of energy use, costs, and environmental impact. The most common desalination system used globally and also applicable to Bangladesh is Reverse Osmosis (RO)
Water treatment Plant price in Bangladesh?
The cost of water treatment plants in Bangladesh varies significantly depending on the type of treatment process and the scale of the plant. For smaller-scale plants designed to serve a limited population or a small industrial area, the prices are relatively lower. In contrast, medium to large-scale plants, which are capable of providing water to entire cities or extensive industrial zones, come at a higher cost due to their advanced technologies and expanded capacity requirements.
At Green Genesis Engineering Limited (GGEL), we specialize in delivering top-tier water treatment plants, expertly tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clients across Bangladesh. Our water treatment plants are equipped with cutting-edge purification systems that efficiently remove harmful contaminants, producing clean, safe water that is not only healthy to drink but also pleasant in taste. Despite the advanced technology and high quality of our systems, we offer competitive pricing to accommodate various budgetary needs. As a leading supplier in the industry, GGEL is committed to delivering reliable and efficient solutions that ensure the highest standards of water quality, without compromising on affordability or excellence.